Ancient Indian Education System vs. Modern Indian Education System
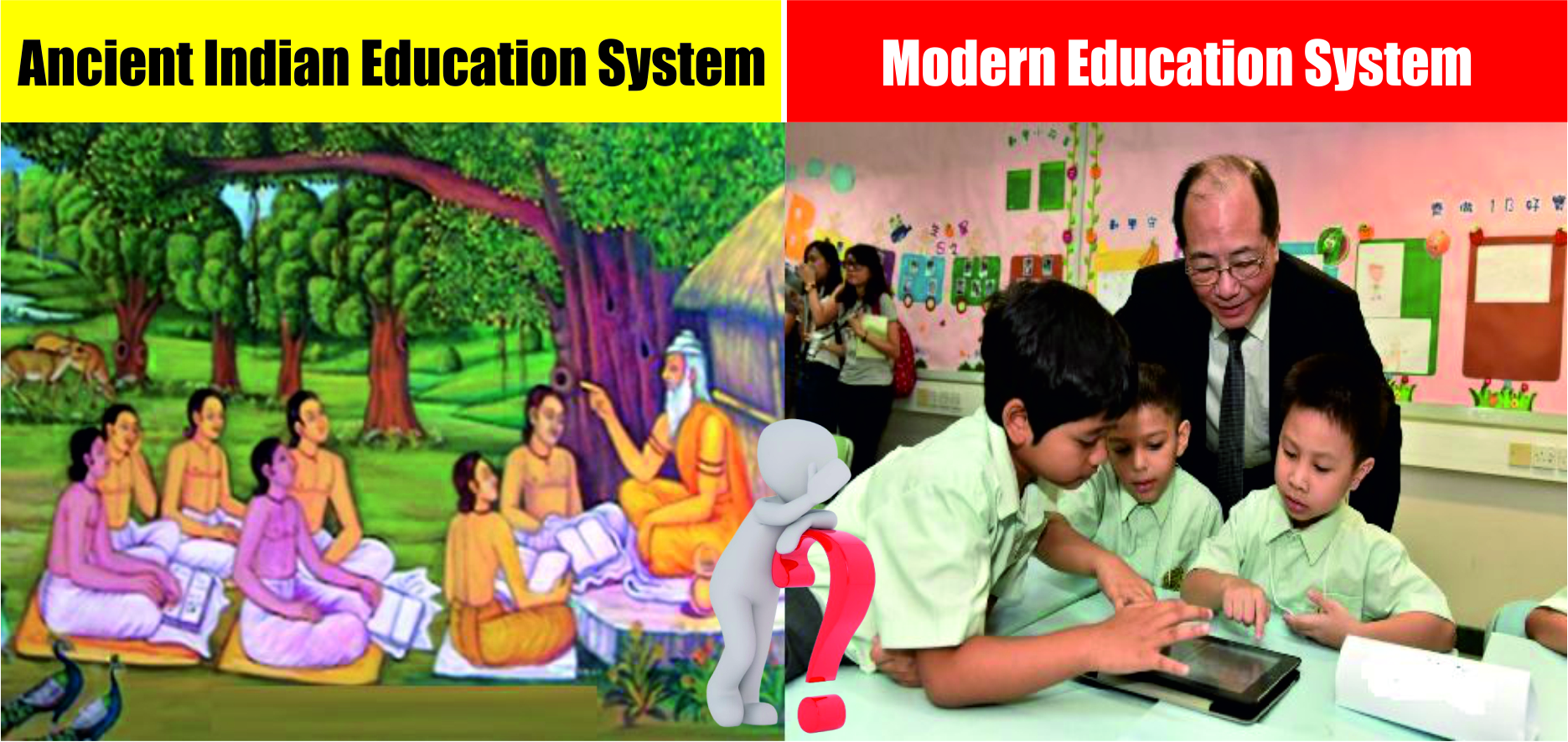
India has always given importance to education, but its methods, objectives and approaches have developed for centuries. The ancient Indian education system was deeply inherent in values, discipline and overall development, while the modern Indian education system emphasizes the structure, certificate and educational performance.
Let’s compare the two systems across key parameters:
Point-by-Point Difference: Ancient vs Modern Education System
- Objective of Education
Ancient: Focus on self-realization, spiritual development, moral development
Modern: Focus on educational success, employment and technological advancement
- Place of Learning
Ancient: Gurukuls, Ashrams, Viharas, Universities like Nalanda, Takshashila
Modern: Schools, colleges, universities, online platforms
- Teacher-Student Relationship
Ancient: Guru-Shishya tradition
Modern: Formal & professional relationship
- Teaching Method
Ancient: Oral transmission, memorization, observation, discussions
Modern: Textbooks, lectures, digital tools, practical labs
- Curriculum Content
Ancient: Vedas, Upanishads, Ayurveda, Astronomy, Philosophy, Archery
Modern: Science, Maths, Languages, Social Studies, Computers
- Medium of Instruction
Ancient: Sanskrit or regional languages
Modern: English, Hindi, and other Indian languages
- Assessment System
Ancient: No formal exams; evaluation based on observation by the guru
Modern: Exams, grading, board tests, competitive entrance exams
- Inclusivity
Ancient: Mostly limited to upper castes and males
Modern: Open and accessible to all genders and social categories
- Use of Technology
Ancient: No technology; learning through nature and interaction
Modern: Smart classrooms, e-learning, educational apps, AI
- Moral & Ethical Focus
Ancient: Strong emphasis on dharma (ethics), discipline, truth, and humility
Modern: Limited focus; moral education optional or minimal
- Vocational Training
Ancient: Embedded in daily life and practical learning
Modern: Offered as a subject (recently gaining more focus through NEP
2020)
- Flexibility in Learning
Ancient: Customized based on interest and aptitude of students
Modern: Predetermined syllabus, stream selection (Science/Arts/Commerce)
- Duration of Education
Ancient: Lifelong, depending on the student’s readiness
Modern: Fixed class-wise system, divided by age and academic year
- Holistic Development
Ancient: Focused on mind, body, and soul
Modern: Mostly focused on academic and professional development
- Cultural Context
Ancient: Deeply rooted in Indian culture, values, and traditions
Modern: More globalized, with Western influence in methods and curriculum
Summary Table
| Feature | Ancient Education | Modern Education |
|---|---|---|
| Holistic Development | Yes | Limited |
| Value-Based Learning | Strong | Weakening |
| Inclusivity | Restricted | Inclusive |
| Formal Certification | No | Yes |
| Technological Integration | No | Yes |
| Teacher-Student Relationship | Deep | Formal |
| Flexibility of Subjects | High | Moderate |
Opinion
The ancient Indian education system preferred values, knowledge and character, making the students not only knowledgeable, but intelligent and moral. The modern education system has brought in structure, access and technological progress, but many times, it remembers the depth of moral and spiritual development.
With the implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, India is now aiming to mix the best in both the world - embracing modern innovations and bringing back the values and flexibility of ancient systems.
For more intensive articles on education reforms, career planning and learning trends, go to www.educationkhoj.com - No. 1 Destination for Educational Services. News | Article | Employment opportunities.



